Most teams now use microservices, where each feature runs as a separate service.
While this improves flexibility, it also creates serious challenges when services communicate directly with each other.
When clients talk to multiple microservices without control, it leads to higher latency, repeated authentication logic, security risks, and complex version management.
Every frontend change can break multiple services, making scaling difficult and costly. If you are trying to learn about NestJs API Gateway, then this blog is for you.
This is where the API Gateway pattern becomes important. An API Gateway acts as a single entry point between clients and backend services.
It handles routing, security, rate limiting, and response aggregation in one place.
In a NestJS microservices architecture, the API Gateway simplifies communication, improves performance, & gives full control over how requests flow across services.
That’s why modern scalable systems depend upon an API Gateway. In this blog, you will learn about API gateway with NestJs & NestJs microservices API gateways.
What Is an API Gateway in NestJS?
A NestJS API Gateway is a central layer that sits between users and microservices. Instead of calling services directly, all requests go through the gateway first.
Using API Gateway with NestJS, you can:
- Route requests to the right microservice.
- Apply authentication and authorization once.
- Transform or validate requests centrally.
- Control traffic and failures easily.
NestJS makes this powerful by using controllers, middleware, guards, & interceptors. These tools help manage routing, security, & orchestration without complex setup.
An API Gateway focuses only on communication and control to keep microservices clean and independent.
Why Choose NestJS for Building a Scalable API Gateway?
NestJS is one of the best frameworks for building a scalable API Gateway because it was designed with enterprise systems in mind.
It offers built-in microservices support, allowing smooth communication using REST, gRPC, or message brokers.
This makes NestJS microservices ideal for distributed systems. The powerful dependency injection system helps keep the gateway clean, modular, & easy to maintain.
This is critical when your API Gateway grows with more routes and services.
With TypeScript, NestJS improves code quality, catches errors early, and makes large teams more productive.
Combined with high performance and clear architecture, scalable API Gateway NestJS solutions are production-ready and future-proof.
How Does API Gateway Architecture Work Using NestJS?
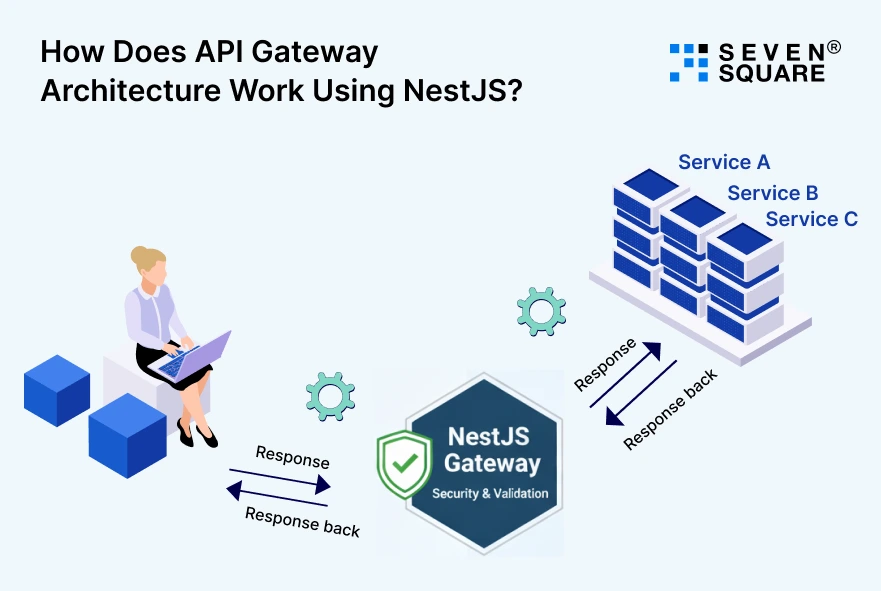
In a typical NestJS microservices API Gateway setup, the request flow looks like this:
Client → API Gateway → Microservices
The API Gateway receives requests, validates them, applies security rules, and forwards them to the correct service.
- Responses can be combined or transformed before returning to the client.
- NestJS supports both synchronous communication (REST, gRPC) and asynchronous communication (message queues, events).
- This flexibility allows teams to design the best API Gateway architecture for performance and scalability.
You can mix REST APIs for user-facing endpoints & message-based patterns for background tasks, all managed cleanly through the gateway.
How to Build an API Gateway Using NestJS?
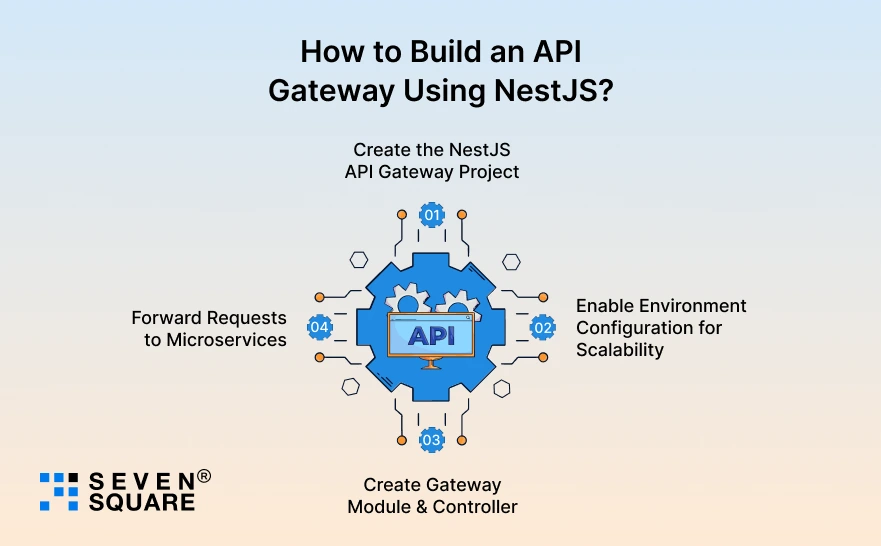
Here you can see API Gateway with NestJS step by step, from project setup to scalable configuration.
Step 1: Create the NestJS API Gateway Project
Install NestJS CLI and create the gateway project:
npm i -g @nestjs/cli
nest new api-gateway
cd api-gateway
npm install @nestjs/microservices @nestjs/config axios
This project will act as the central API Gateway for all microservices.
Step 2: Enable Environment Configuration for Scalability
Create a .env file:
USER_SERVICE_URL=http://localhost:3001
ORDER_SERVICE_URL=http://localhost:3002
JWT_SECRET=supersecretkey
Enable environment support:
// app.module.ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { ConfigModule } from '@nestjs/config';
import { GatewayModule } from './gateway/gateway.module';
@Module({
imports: [
ConfigModule.forRoot({ isGlobal: true }),
GatewayModule,
],
})
export class AppModule {}
This setup helps scale across dev, staging, and production environments.
Step 3: Create Gateway Module & Controller
// gateway/gateway.module.ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { GatewayController } from './gateway.controller';
import { GatewayService } from './gateway.service';
@Module({
controllers: [GatewayController],
providers: [GatewayService],
})
export class GatewayModule {}
// gateway/gateway.controller.ts
import { Controller, Get, Post, Req } from '@nestjs/common';
import { GatewayService } from './gateway.service';
import { Request } from 'express';
@Controller()
export class GatewayController {
constructor(private readonly gatewayService: GatewayService) {}
@Get('users')
getUsers() {
return this.gatewayService.forward('users');
}
@Post('orders')
createOrder(@Req() req: Request) {
return this.gatewayService.forward('orders', req.body);
}
}
Step 4: Forward Requests to Microservices
// gateway/gateway.service.ts
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import axios from 'axios';
import { ConfigService } from '@nestjs/config';
@Injectable()
export class GatewayService {
constructor(private config: ConfigService) {}
async forward(service: string, data?: any) {
const serviceMap = {
users: this.config.get('USER_SERVICE_URL'),
orders: this.config.get('ORDER_SERVICE_URL'),
};
const url = serviceMap[service];
const response = await axios.post(url, data);
return response.data;
}
}
- This is the core of a NestJS API Gateway tutorial.
- Clean routing.
- Centralized communication.
How to Implement Smart Routing & Service Discovery?
It improves routing and resilience using NestJS routing microservices best practices.
Dynamic Routing Between Services
// gateway/service-registry.ts
export const SERVICE_REGISTRY = {
users: ['http://localhost:3001'],
orders: ['http://localhost:3002'],
};
// gateway/load-balancer.ts
export function pickService(instances: string[]) {
return instances[Math.floor(Math.random() * instances.length)];
}
// gateway/gateway.service.ts (updated)
import { SERVICE_REGISTRY } from './service-registry';
import { pickService } from './load-balancer';
async forward(service: string, data?: any) {
const instance = pickService(SERVICE_REGISTRY[service]);
const response = await axios.post(instance, data);
return response.data;
}
Handling Service Failures
async forward(service: string, data?: any) {
try {
const instance = pickService(SERVICE_REGISTRY[service]);
const response = await axios.post(instance, data);
return response.data;
} catch (error) {
return {
error: 'Service temporarily unavailable',
service,
};
}
}
- Prevents system crashes.
- Improves reliability.
- Business-friendly behavior.
How to Secure a NestJS API Gateway Properly?
Security is important. It implements a secure API Gateway NestJS approach.
JWT Authentication at Gateway Level
npm install @nestjs/jwt passport-jwt @nestjs/passport passport
// auth/jwt.strategy.ts
import { PassportStrategy } from '@nestjs/passport';
import { Strategy, ExtractJwt } from 'passport-jwt';
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
@Injectable()
export class JwtStrategy extends PassportStrategy(Strategy) {
constructor() {
super({
jwtFromRequest: ExtractJwt.fromAuthHeaderAsBearerToken(),
secretOrKey: process.env.JWT_SECRET,
});
}
async validate(payload: any) {
return payload;
}
}
Protect Routes with Guards
// auth/jwt.guard.ts
import { AuthGuard } from '@nestjs/passport';
export class JwtAuthGuard extends AuthGuard('jwt') {}
// gateway/gateway.controller.ts
import { UseGuards } from '@nestjs/common';
import { JwtAuthGuard } from '../auth/jwt.guard';
@UseGuards(JwtAuthGuard)
@Get('users')
getUsers() {
return this.gatewayService.forward('users');
}
Request Validation & Unauthorized Access Prevention
// main.ts
import { ValidationPipe } from '@nestjs/common';
app.useGlobalPipes(new ValidationPipe());
- Centralized authentication.
- No security duplication in microservices.
- Strong NestJS authentication gateway design.
Here’s the Complete GitHub Code to Implement an API Gateway with NestJs.
What’s Our Expertise in Implementing Scalable API Gateways Using NestJS?
- We help businesses replace complex setups with flexible API Gateway architecture using NestJS microservices.
- Our solutions support REST, gRPC, and message-based communication for modern, scalable backend systems.
- We build an API Gateway with NestJS that simplifies microservices communication and reduces long-term development overhead.
- Our team focuses on performance optimization, smart routing, and load balancing for scalable API Gateway NestJS solutions.
Want to Implement API Gateways in NestJS? Contact Us Today!
API Gateway vs Dedicated Tools (Kong, NGINX, AWS API Gateway)
A NestJS API Gateway vs Kong comparison shows that NestJS is often better when:
| Feature | NestJS API Gateway | Kong API Gateway | NGINX | AWS API Gateway |
| Customization Flexibility | Full control using TypeScript and custom logic. | Limited to plugins and configurations. | Limited & mostly config-based. | Limited, AWS-managed rules. |
| Microservices Integration | Built for NestJS microservices architecture. | Good, but setup can be complex. | Requires extra configuration. | Works well with AWS services only. |
| Authentication & Security | Custom JWT, OAuth, guards, and middleware. | Plugin-based authentication. | Manual security configuration. | Built-in AWS IAM & Cognito. |
| Scalability | Scales with application architecture. | Highly scalable. | Highly scalable. | Auto-scales within AWS. |
| Performance Control | High, logic optimized at the code level. | High but less flexible. | Very high & low-level control. | High but limited customization. |
| Ease of Development | Developer-friendly & clean architecture. | Moderate learning curve. | Steep learning curve. | Easy but AWS-dependent. |
Is NestJS the Right Choice for Your API Gateway?
If you are building a modern, scalable application and want full control over routing, security, and performance, NestJS is a strong choice for API Gateway implementation.
Use NestJS API Gateway when:
- You use microservices.
- You need custom logic and flexibility.
- You want a scalable and maintainable architecture.
Overall, NestJS offers the perfect balance of performance, scalability, and developer productivity to build modern API-driven systems.
FAQs
- An API Gateway in NestJS is a centralized service that manages routing, security, and communication between clients and microservices.
- Yes. NestJS supports scalable architecture, microservices, authentication, & performance optimization to make it suitable for enterprise systems.
- Yes, with proper caching, load balancing, and async communication, a NestJS API Gateway can handle high traffic efficiently.
- Microservices communicate through REST, gRPC, or message-based patterns, all managed and controlled by the NestJS API Gateway.